
Value Proposition Design Summary
This book makes a big point of making sure you review and understand Business Model Canvas before you start. If you haven’t done so, it is highly recommended that you refresh your memory of Business Model Canvas.
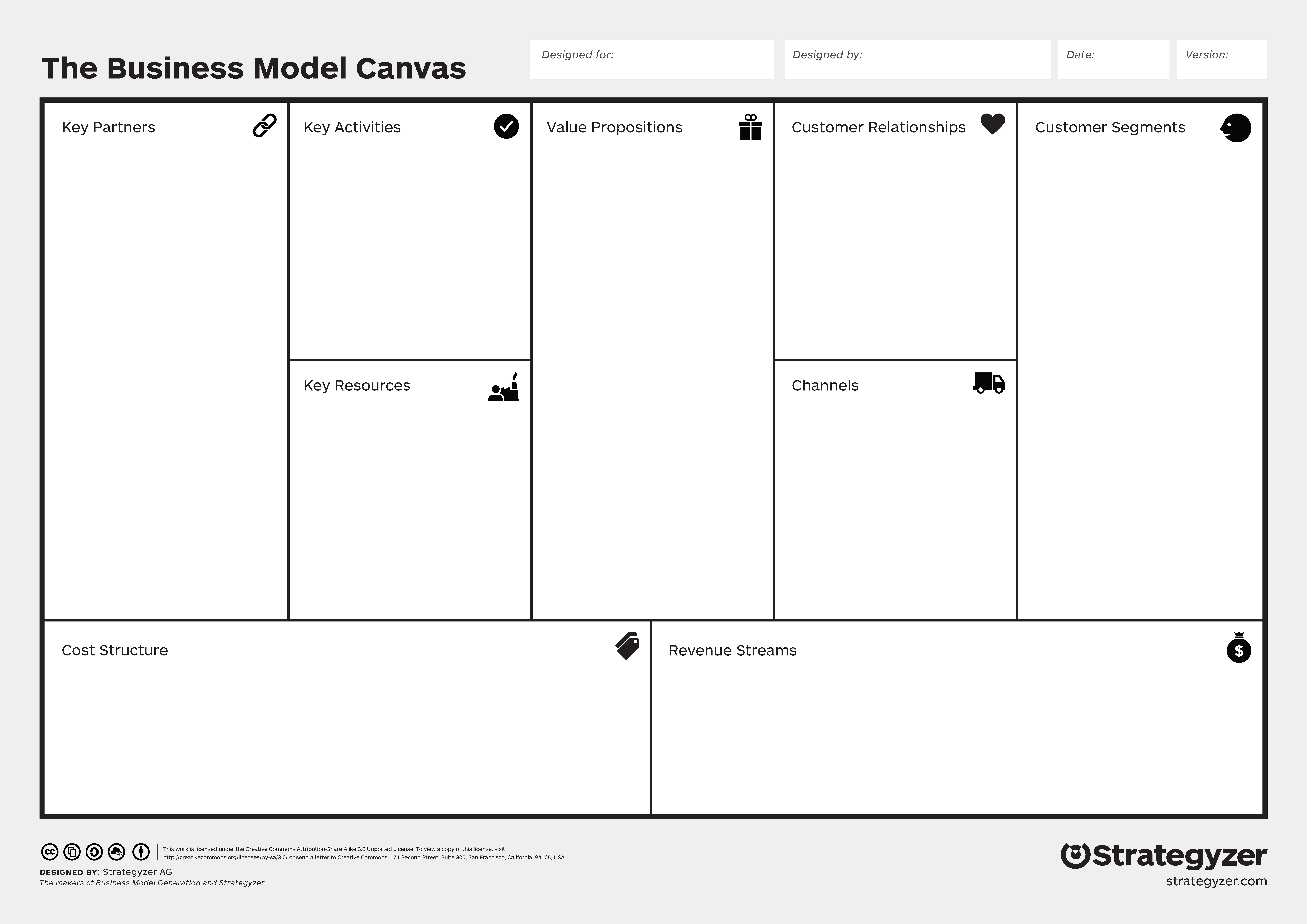
Download an original high-res PDF of this image directly from the Strategyzer website. OR you can download an easier to edit PowerPoint version of Business Model Canvas here.
You’ll love this book if…
“You’ll love Value Proposition Design if you’ve been overwhelmed by the task of true value creation, frustrated by unproductive meetings and misaligned teams, involved in bold shiny projects that blew up or disappointed by the failure of a good idea. Value proposition design will help you successfully understand the patterns of value creation, leverage the experience and skills of your team and avoid wasting time with ideas that won’t work. Design, test, and deliver what customers want.”
Canvas
“The value proposition canvas has two sides. With the customer profile you clarify your customer understanding. With the value map you describe how you intend to create value for that customer. You achieve fit between the two and one meets the other.”
Side 1: Map the client’s job pains and gains
Page 15 lists questions such as: how do your customers define too costly, taking too much time or requires too much effort? What gives them a headache? Also consider loss of faith, power, trust, or status? What do they fear?
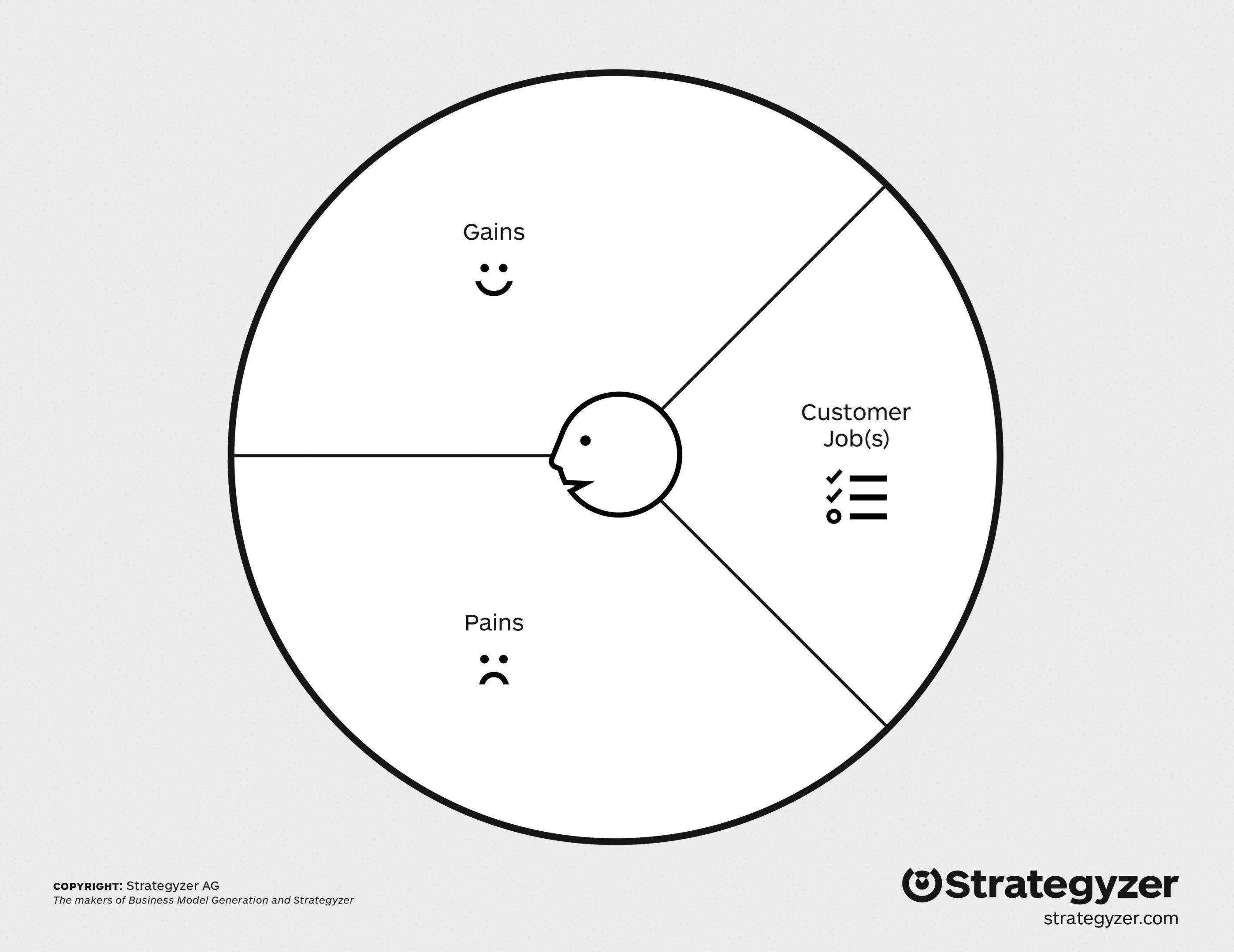
Download an original high-res PDF of this image directly from the Strategyzer website.
Common mistakes in mapping job pains and gains
- Missing several customer segments into one profile.
- Mixing jobs and outcomes.
- Focusing on job function only and forgetting social and emotional implications.
- Listing jobs pains and gains with your value proposition in mind.
- Identifying too few jobs pains and gains
Side 2: Map the Value Proposition
List your products and services. Outline the pain relievers. Outline the game creators. Rank by order of importance.
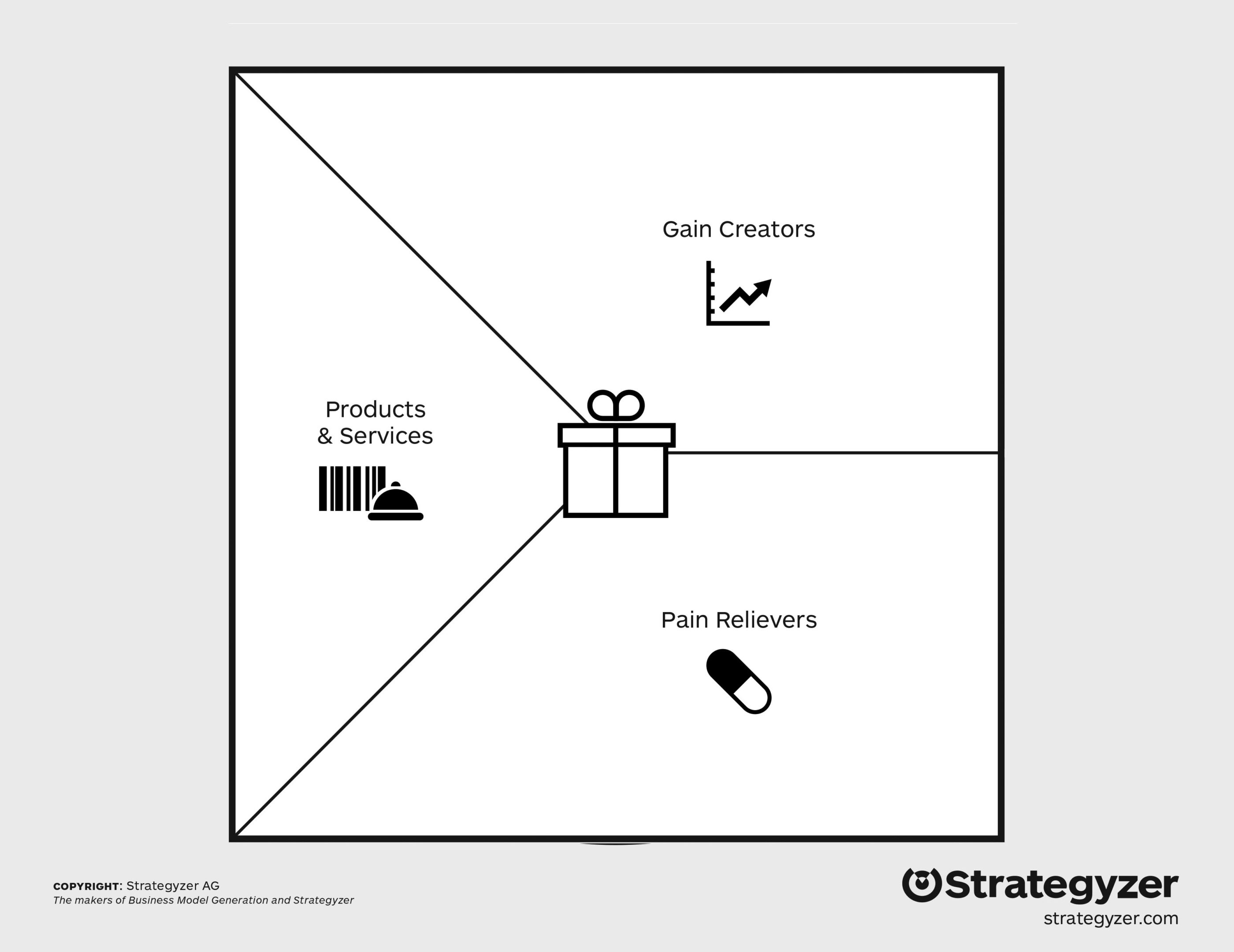
Download an original high-res PDF of this image directly from the Strategyzer website.
Common mistakes in mapping value proposition
- Listing all of your products and services instead of those targeted at a specific segment.
- Adding products and services to the pain reliever and game creator fields.
- Offering pain and gain creators that have nothing to do with a customer profile.
- Making an unrealistic attempt to address all customer pains and gains.
Three kinds of fit.
- On paper.
- In the market.
- In the bank.
Design
10 characteristics of great value propositions
- Embedded in great business models.
- Focus on jobs pains and gains that matter most to customers.
- Focus on unsatisfied jobs pains and gains.
- Target a niche number of jobs pains and gains but do so extremely well.
- Go beyond functionality and address emotions and social implication.
- Align with our customers measure success.
- Focus on solutions that a lot of people have or that some will pay a lot of money to solve.
- Differentiated from competition.
- Out performs the competition.
- Is difficult to copy.
Starting points
- Page 88 and 89 list some good questions for brainstorming new business directions. Reviews pushing vs. pulling.
- A “push” defined solution means you’re starting point is the invention or proprietary technology you’ve developed.
- A ”pull” defined solution means you’re starting with the market problem and trying to create a solution.
- The book feels most often there is a little of both in developing a value proposition.
Six techniques to gain customer insight
- Be a data detective.
- Conduct Interviews.
- Direct observation or anthropology.
- An impersonator that spends time in your customer shoes and tests your product.
- Co-creation with a customer.
- Customer participation in an experiment.
Identify behavior patterns (create personas)
Take all the data from your customer insights group and segment classifying each persona into a master profile. Build and design prototypes around the profiles.
Find your early evangelist
This is a customer who has cobbled together an interim solution to the problem and is desperately looking for a better solution. Consequently, they are willing and able to take risks on a new product or service via experimentation and learning and has or can acquire a budget.
Reinvent by shifting from products to services
Example in the book discusses how Hilti tools changed focus from selling tools to helping contractors deliver projects on time and avoiding financial penalties due to broken malfunctioning or stolen tools. This involves delivery vans mapping of active jobsites and creating key customer relationships. Services achieve higher margins, reoccurring revenues and better differentiation in a product market.
Test
10 testing principles
- Evidence trumps opinion.
- Reduce risk and learn faster by embracing failure.
- Test early and refined later.
- Experiments do NOT equal reality.
- Balance learnings and vision.
- Test the biggest deal killers early.
- Understand customers first.
- Make it measurable.
- Not all facts are equal (customers may say one thing but do another).
- Test irreversible decisions twice as much.
Apply lean start up principles
Create a Build, Measure, Learn loops. BML
Testing step-by-step
- What needs to be true for your idea to work?
- What hypotheses or assumptions are you making that could kill your business? Test them first.
- The faster you Iterate through your BML Loop the faster you will learn. This is called your cycle time.
Avoid the following data traps:
- False positives and negatives – Testing for things that are not there or not seeing things that are there.
- Local Maximum Trap – you optimize features for a local niche ignoring the larger opportunity.
- The exhausted maximum trap – do you think an opportunity is larger than it is. Make sure your design test proof potential beyond immediately addressed test subjects.
- The wrong data – The customers you testing are not interested because you tested the wrong market.
Create an experiment library
Use this to test the sales funnel from top to bottom:
- Overall interest.
- Priorities and preferences.
- Willingness to pay.
The purpose of the experiment library is to move customers through the sales funnel toward a “call to action” or CTA, which is to pay. In some cases they might perform certain actions towards paying but not actually pay for the product (pop-up says “sold out”).
Ad tracking
Create a link with a test ad and track results. Understand that in a new market people will not be searching for words for a market that does not exist.
MVP options
- Data sheet.
- Brochure.
- Storyboard.
- Landing page.
- Product box.
- Video.
- Learning functioning prototype.
- Wizard of Oz (A front that looks like the real working thing, but you perform that which should be automated tasks manually in the background). Life-size experiments. Prototype spaces.
Landing page MVP
- The goal is to validate one or more hypotheses, not collect emails or sell which is simply a byproduct of the Experiment.
- Should have a headline, a value proposition, and a call to action at the bottom.
- Use split testing.
Innovation games
Much to my chagrin one of the concepts outlined is the speedboat. Deliberately hold customers back from completing their jobs, to see what causes the most pain. It’s like putting anchors on a speedboat.
Other testing ideas
- Buy a feature.
- Mock sales.
- Pre-sales.
Evolve
- Create alignment
- Measure and monitor
- Improve relentlessly
- Reinvent yourself constantly
Further Info
- You can access original info, tons of free guides, question lists, planning tools and more for Value Proposition Design directly from the Strategyzer website.
- You can download an easier to edit PowerPoint version of Business Model Canvas here.
- And of course please make sure to buy a copy of this book by clicking the purchase link below:

Value Proposition Design: How to Create Products and Services Customers Want (The Strategyzer Series)
Download a Preview
To see how much information is packed into this book, the authors have generously provided this incredible PDF book preview. I included just a few select images from the preview in the gallery below just to give you an idea.
Author Bio
Benjamin Arritt
Share:
Follow Us:
Most Popular


10+ PERSONAL CRM OPTIONS REVIEWED

10 OUTSOURCED BDR SALES AGENCIES COMPARED

FRACTIONAL MARKETING: EFFICIENT BUSINESS GROWTH
Subscribe To Our Newsletter
No spam. Curated directories & articles about business, startups and templates.
MENU
Related Posts

How to Build a High-Performing Marketing Stack for CMO Success
Dive into our blog post to learn how chief marketing officers can transform from brand champions to revenue drivers and customer whisperers through a strategic

10+ PERSONAL CRM OPTIONS REVIEWED
Yes, there are “solutions,” but nothing is perfect. Here is the path of what I evaluated, what I liked, what I didn’t and why. I

10 OUTSOURCED BDR SALES AGENCIES COMPARED
I interviewed several of the top performers according to Clutch, but this was not my exclusive source. Here’s why: some smaller companies, without as much

FRACTIONAL MARKETING: EFFICIENT BUSINESS GROWTH
Fractional marketing involves hiring fractional marketers, or part-time marketing professionals. This way businesses can leverage specialized expertise while reducing the costs associated with a full-time
